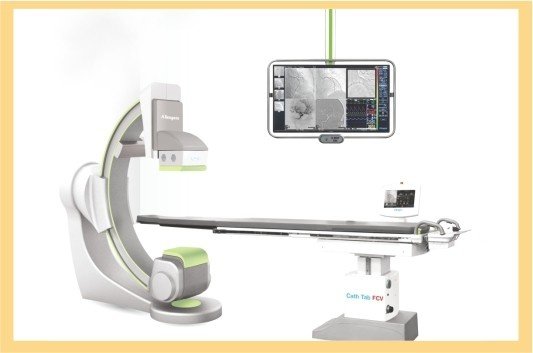
ANGIOGRAPHY
ANGIOGRAPHY
Angiography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. It's commonly used to diagnose and treat various conditions related to blood vessels, such as blockages, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
Common types of angiography procedures include:
- Coronary Angiography: This procedure focuses on the coronary arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle. It's often used to diagnose blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries, which can lead to conditions like angina or heart attacks.
- Peripheral Angiography: This procedure examines the blood vessels outside of the heart and brain, typically in the arms, legs, abdomen, or pelvis. It's used to diagnose conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD), aneurysms, or blood clots.
- Cerebral Angiography: Also known as cerebral arteriography or intracranial angiography, this procedure focuses on visualizing the blood vessels in the brain. It's used to diagnose conditions such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), or strokes.
- Pulmonary Angiography: This procedure examines the blood vessels in the lungs. It's commonly used to diagnose pulmonary embolisms, which occur when blood clots travel to the lungs from other parts of the body.
- Renal Angiography: This procedure examines the blood vessels in the kidneys. It's used to diagnose conditions such as renal artery stenosis, which can lead to high blood pressure or kidney damage.
- Aortography: This procedure focuses on visualizing the aorta, the largest artery in the body. It's used to diagnose conditions such as aortic aneurysms or dissections.