Stress-Echo
Stress-Echo
A stress echocardiogram, commonly known as stress-echo, is a diagnostic procedure that combines ultrasound imaging of the heart with physical stress to assess heart function and blood flow. During the test, patients undergo echocardiography while at rest and then again after physical exertion induced either by exercise or medication. This allows healthcare providers to evaluate how the heart responds to stress, aiding in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, and other cardiac conditions. The test is non-invasive and helps guide treatment decisions by providing valuable information about the heart's performance under different conditions.
Here's a brief description of what might be involved in a stress-echo procedure at Narayan Swaroop Hospital:
- Preparation: Before the test, the patient may be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours, depending on the hospital's protocol. They may also need to refrain from certain medications that could interfere with the test. Patients should wear comfortable clothing and appropriate footwear for exercise.
- Baseline Echocardiogram: The procedure starts with a baseline echocardiogram, where ultrasound images of the heart are taken while the patient is at rest. This provides a comparison for the images obtained during stress.
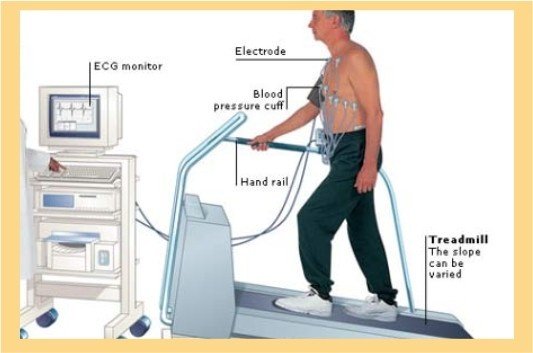
- Stress Induction: The patient undergoes a stress-inducing activity, typically either walking on a treadmill or receiving medication that simulates the effects of exercise on the heart. The level of stress is gradually increased to the desired target heart rate or until symptoms occur.
- Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the stress portion of the test, the patient's heart rate, blood pressure, and symptoms are closely monitored by medical staff.
- Stress Echocardiogram: While the patient is still experiencing stress, another set of echocardiogram images is taken to assess the heart's function under stress conditions. This allows the cardiologist to evaluate any changes in heart function or blood flow that may indicate underlying heart disease.